In corporate environments, the use of external storage devices such as USB drives, external hard disks, CDs, or DVDs represents a significant risk to information security and regulatory compliance. macOS provides native mechanisms to restrict these devices through configuration profiles, allowing organizations to enforce strict media control policies without installing additional agents or relying on monitoring scripts.
This approach is based on a .mobileconfig configuration profile that applies restrictions to macOS system behavior—specifically through the SystemUIServer component—controlling how the operating system reacts when external storage media is connected.
When applied, the profile can detect the insertion of external media, prevent it from being mounted, automatically eject it, and display a system notification informing the user that the device is blocked. Other peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, or charging cables, are not affected, as long as they are not recognized by macOS as storage devices.
Blocked media types #
Using this configuration, macOS can restrict multiple types of removable storage, including external USB hard drives, USB flash drives, CDs and DVDs, optical media, and other mass storage devices recognized by the system. When one of these devices is connected, macOS automatically ejects it and prevents it from being mounted, making it inaccessible to the user.
Configuration #
Once in the Applivery dashboard, head to the Device Management section and select Policies (1). Choose the policy where you want to apply this setting.
From the left-hand menu, navigate to the + Add configuration (2) option and then choose Media Management: Allowed Media (3).
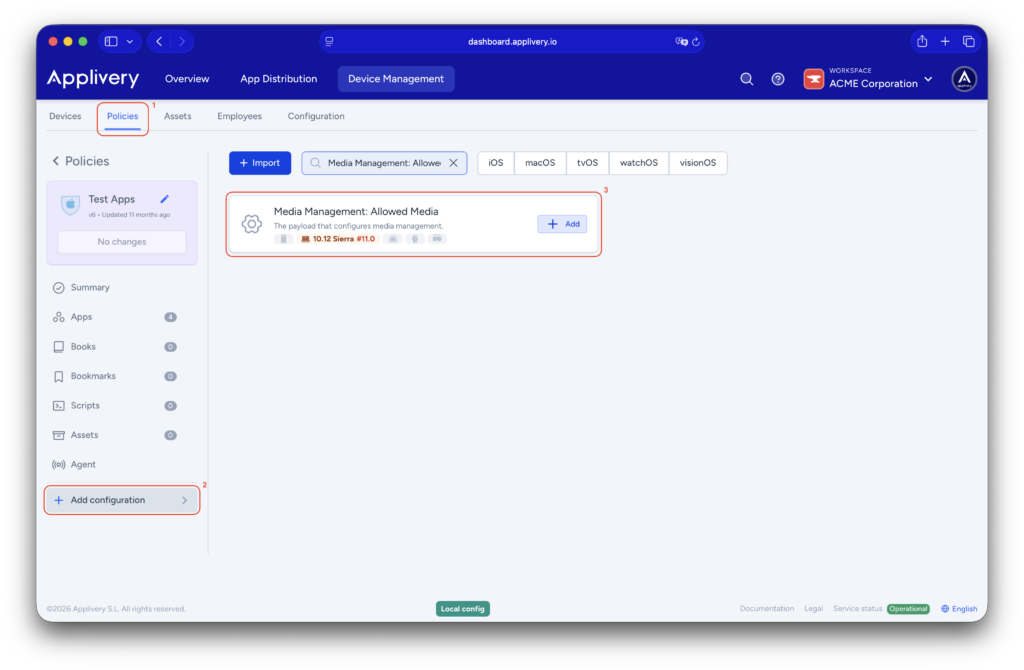
This payload is structured into three distinct sections, each applied at a different stage of the device lifecycle and serving a specific security purpose.
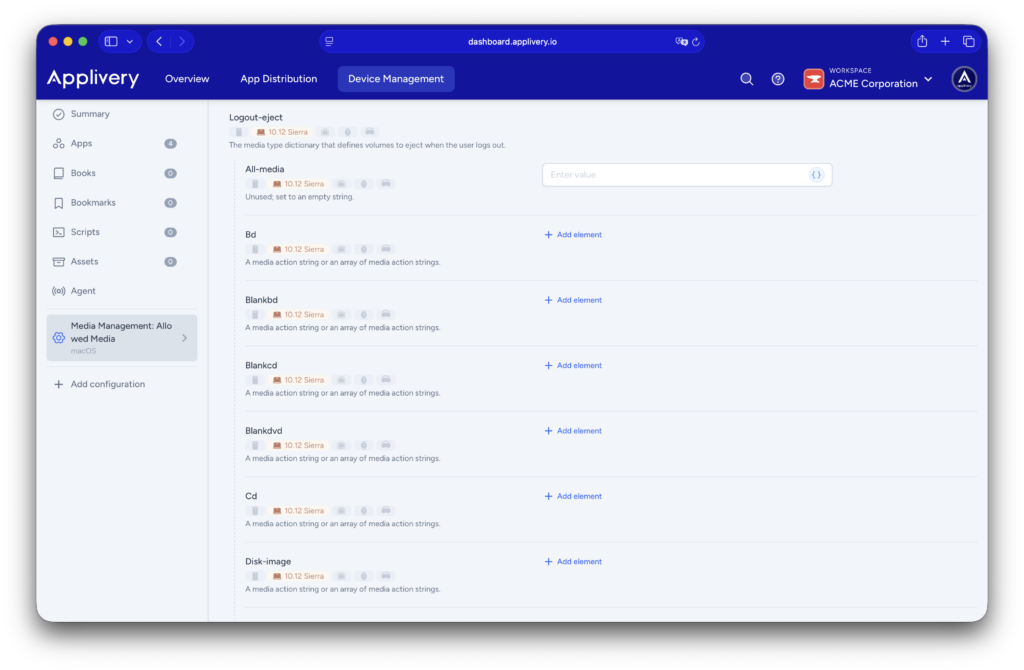
Logout eject: device control at user logout #
This section defines which storage devices are automatically ejected when a user logs out of macOS. It does not block device usage during an active session but ensures that no external storage remains mounted once the user session ends.
This is particularly useful on shared devices, preventing external drives from being accessed by subsequent users and reinforcing security without impacting day-to-day workflows. For example, external hard drives can be configured to be automatically ejected upon logout.
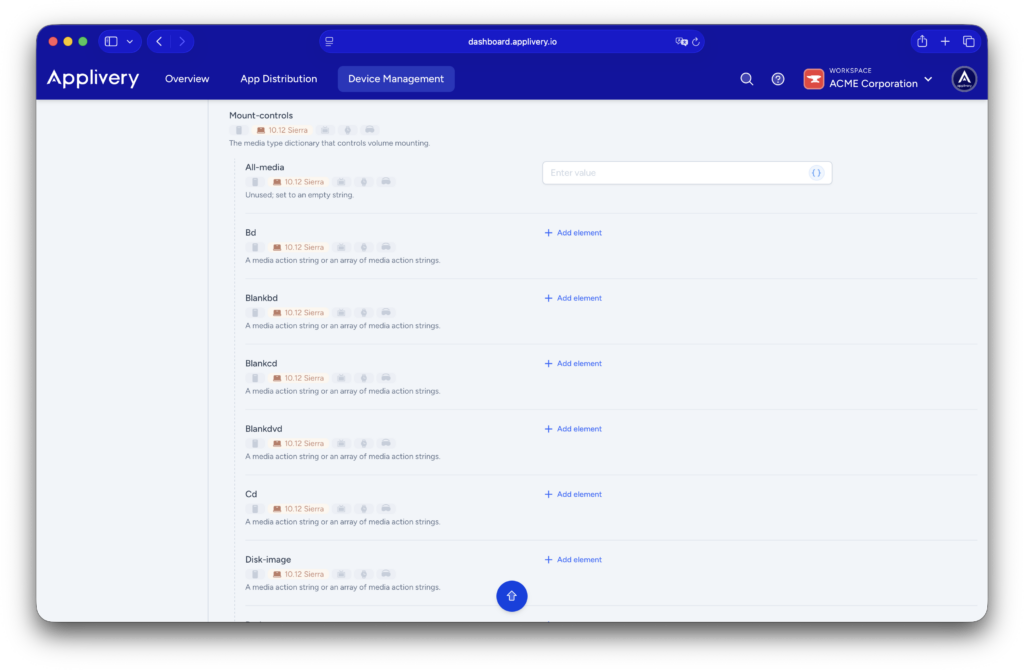
Mount controls: control of device mounting #
This is the most critical section of the payload, as it determines whether a storage device can be mounted at all when it is connected. macOS evaluates these rules immediately upon device insertion. Administrators can completely block access, allow read-only access, or permit full usage depending on the organization’s requirements.
Mount-controls are commonly used to block USB drives to prevent data exfiltration, allow optical media in read-only mode, or strictly control non-corporate storage devices. If a device type is blocked here, it cannot be used under any circumstances, regardless of any other configuration sections.
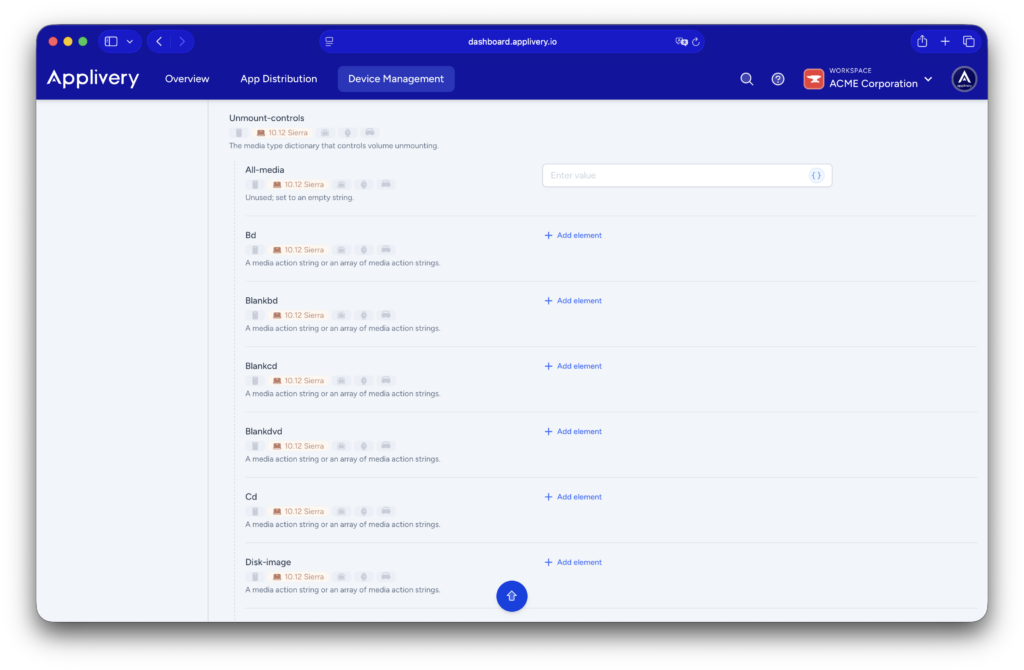
Unmount controls: manual device ejection control #
This section governs whether a user is allowed to manually eject a device that is already mounted. It does not affect the initial connection or mounting of the device.
Typical use cases include preventing accidental disconnection of critical network drives or protecting specific corporate environments where manual ejection could cause operational issues.
Functional summary #
Section
Applied when
Main function
Logout eject
User logout
Automatic device ejection
Mount controls
Device connection
Allow or block mounting
Unmount controls
Manual ejection
Allow or block device unmounting
Available actions #
Within the logout eject, mount controls, and unmount controls sections, administrators can define how macOS reacts to each media type:
- The Authenticate action allows device usage only after the user successfully authenticates with their macOS credentials. This option is suitable when access should be restricted to authorized users without fully blocking the device.
- The Read-only action permits access to files while preventing any data from being written to the device. Users can view and copy files from the device to the Mac, but cannot modify files or copy corporate data to external storage, making this option ideal for preventing data leakage.
- The Deny action fully blocks the device, preventing it from being mounted or accessed in any way. In this case, the device may briefly appear and then disappear, or not appear at all. If a media type is set to Deny in Mount-controls, no other configuration will override this behavior.
- The Eject action allows normal usage during the active session but automatically ejects the device when the configured event occurs, such as user logout. This option is commonly used on shared Macs to ensure external devices are not left mounted.
Action
Access allowed
Write allowed
Auth required
Typical use
Authenticate
✅
✅
✅
User-based control
Read-only
✅
❌
❌
Prevent data exfiltration
Deny
❌
❌
❌
Total blocking
Eject
✅ (temporary)
✅
❌
Cleanup at logout
General recommendation #
In most Applivery-managed corporate environments, media control policies typically rely on mount controls as the primary enforcement mechanism, complemented by logout eject as an additional safeguard. Unmount controls are usually reserved for very specific scenarios.
Combining these sections appropriately allows organizations to implement strong security controls without unnecessarily impacting user productivity.
Restriction removal behavior #
If the configuration profile is removed from the device, a system restart is required for all restrictions to be fully lifted. Until the restart occurs, macOS may continue enforcing the media block. This behavior is inherent to the operating system and should be considered during troubleshooting or policy changes.
By distributing configuration profiles through Applivery, organizations can natively and effectively block external storage devices on macOS in a centralized, scalable, and non-intrusive manner. This approach improves data security, integrates seamlessly with macOS, and provides IT teams with precise control over removable media usage while maintaining a balanced user experience.