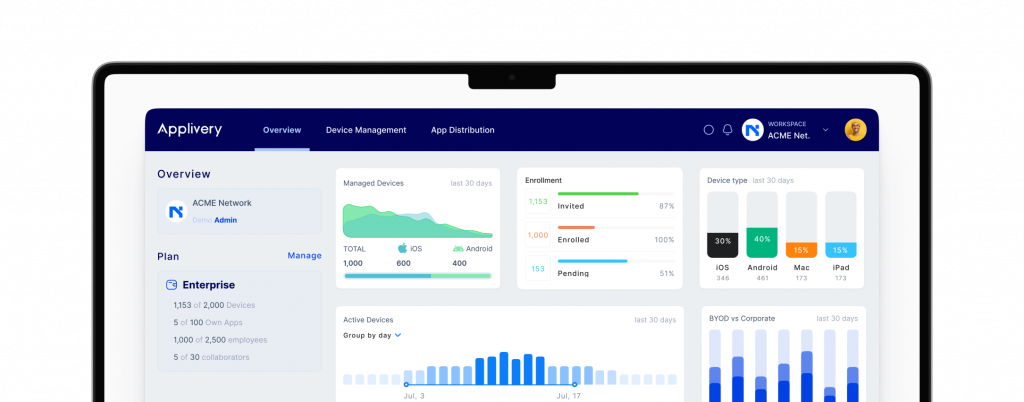
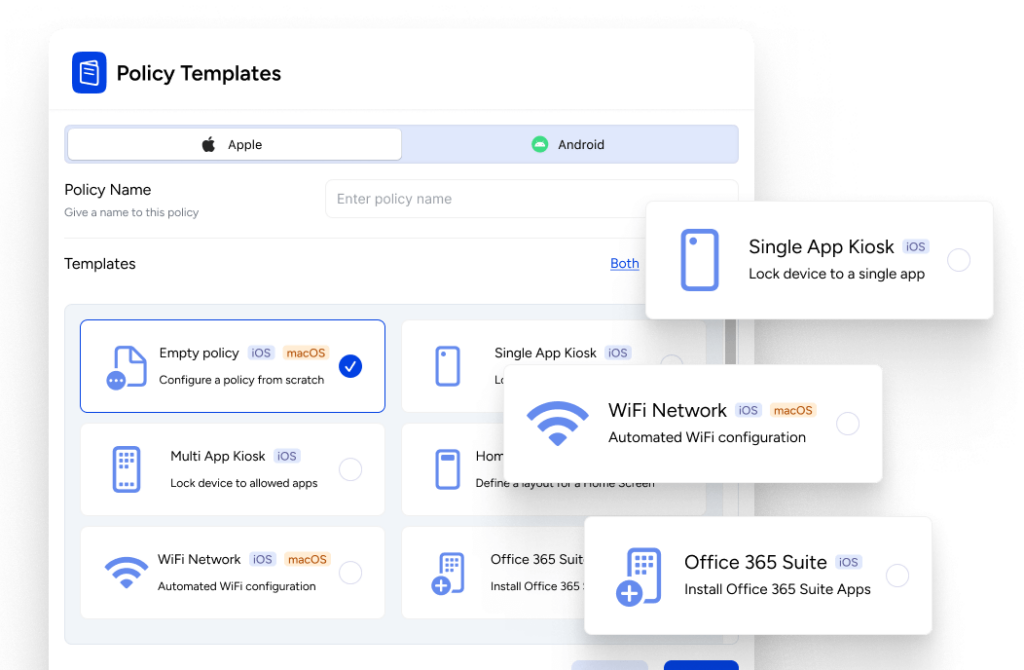
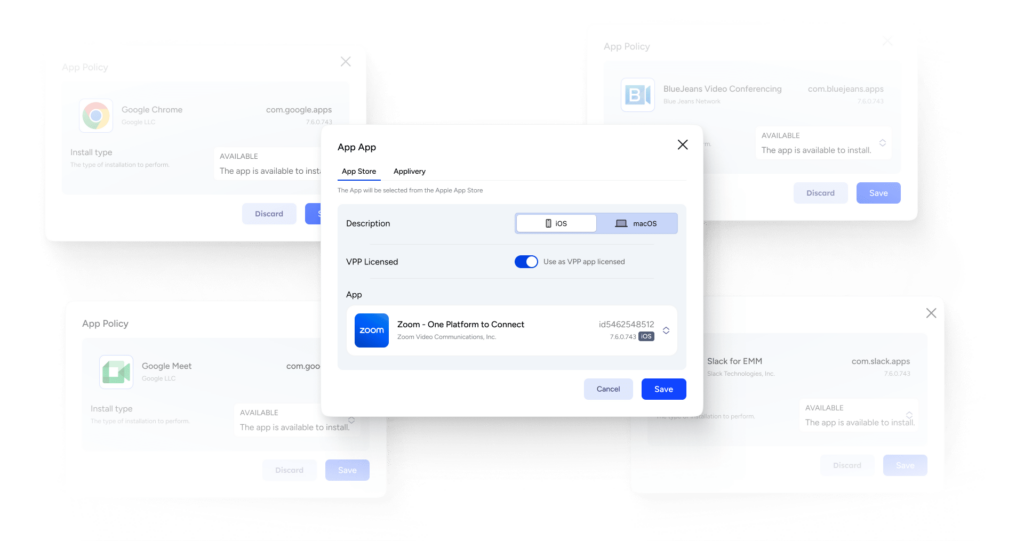
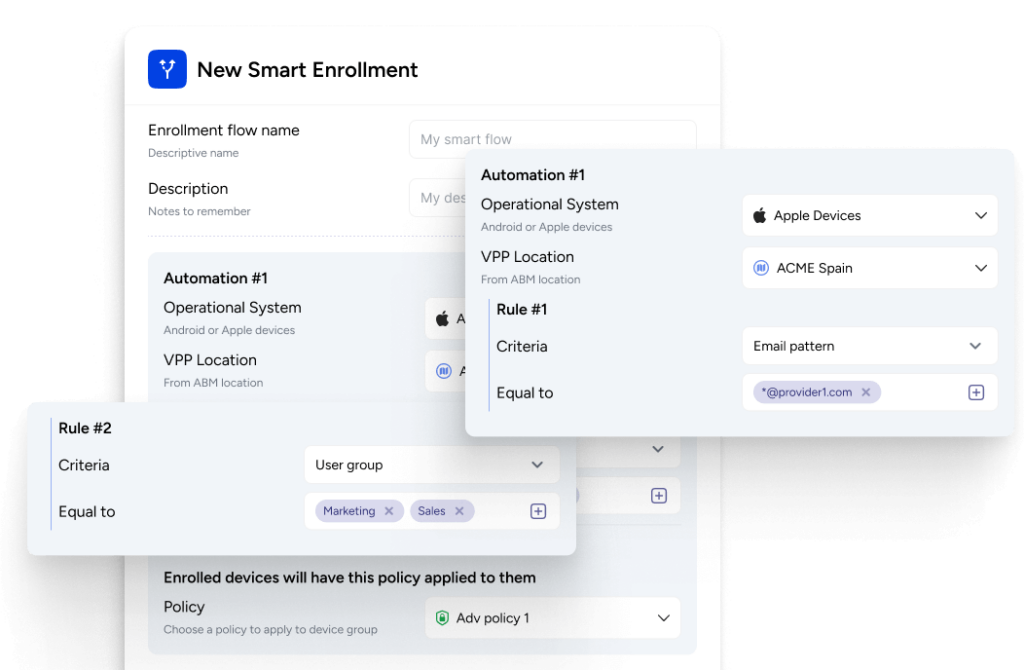
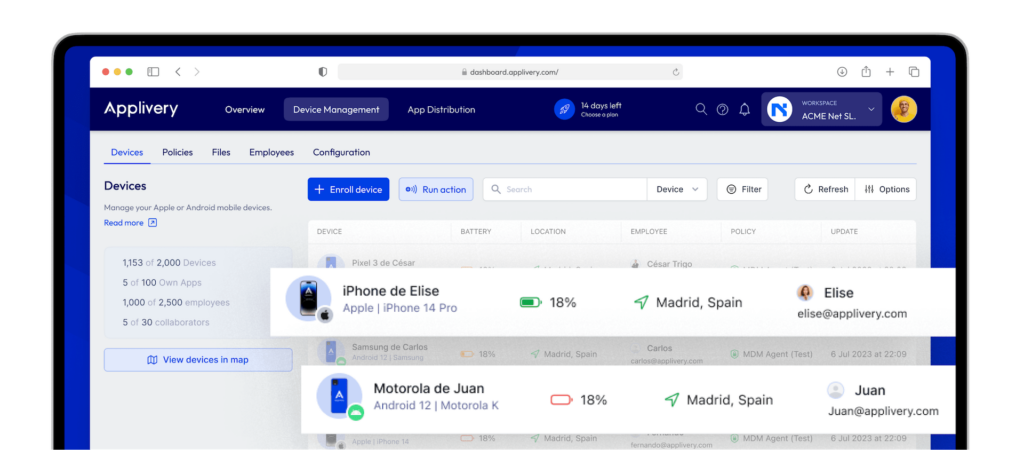
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is like a software superhero for organizations. Its main job is to take care of all the mobile devices we use, like smartphones, tablets, and laptops, and keep them safe and well-behaved. It does this by helping with a bunch of important tasks:
- Installing and Managing Apps: MDM can put apps on our devices and keep them up to date.
- Tweaking Device Settings: It’s like the control panel for our devices, letting organizations set rules and preferences.
- Watching Device Activity: MDM keeps an eye on what we do with our devices, which can be helpful.
- Protecting Against Bad Stuff: It guards our devices from things like viruses and data leaks.
- Emergency Cleanup: If a device goes missing, MDM can erase everything on it remotely.
Now, MDM usually hangs out in big companies where lots of devices need looking after. But it’s not exclusive; even small businesses and regular folks can use it to keep their devices safe.
The thing is, MDM isn’t a one-size-fits-all deal. It can do different things depending on who made it and what a company needs. Some common things it does include:
- Getting New Devices Ready: When a new device joins the team, MDM helps set it up.
- App Management: It helps the organization put useful apps on our devices and keeps them in line.
- Settings Control: MDM lets the company tweak how our devices work, like making sure they’re secure.
- Finding Lost Devices: If you lose your device, MDM can help track it down.
- Device Safety: It’s like a bodyguard for our devices, protecting them from harm.
- Emergency Reset: If a device gets kidnapped (or just lost), MDM can wipe everything clean from afar.
Using MDM is like giving your devices a security boost. Here’s why it’s a good idea:
- Top-Notch Security: MDM makes sure our devices stay safe from bad stuff like viruses and data leaks.
- More Productivity: It helps organizations get things done faster by managing apps and giving remote access to work stuff.
- Saving Money: MDM makes it cheaper to handle mobile devices because it puts everything in one place.
But before diving into MDM:
- Remember, MDM features can change depending on the company and what you need.
- It can be a bit tricky to set up and use in old companies of MDM, so having an IT expert on hand is smart, but with Applivery you can simplify your life as anyone can manage the platform.
If you’re not sure if MDM is right for your company, talk to us—we’ll point you in the right direction.