Check the availability in our pricing page.
metadata field. Understanding SCIM Attribute Storage #
attributesHistory. This object tracks every attribute received from SCIM, whether or not it is currently mapped to metadata. SCIM Attributes History #
attributesHistory object contains all SCIM attributes in the following structure:
type IProviderSCIMAttributesHistory = {
namespace: string
key: string
}
This object is populated automatically with all attributes provided in SCIM requests. Its purpose is to serve as a complete record of any field that can potentially be mapped.
Custom Attribute Mapping #
To map SCIM fields into the user’s metadata, you can define a custom mapping through the mappedAttributes property in the SCIM configuration model.
type IProviderSCIMCustomAttributes = {
name: string
attributes?: {
namespace?: string
key: string
}[]
}
Each mapping entry supports the following fields:
- Name: The key under which the mapped value will be stored inside the user’s metadata.
- Attributes: A list of SCIM attributes (optionally specifying their namespace/schema) that will be used to generate this metadata value.
Resolution rules #
When resolving which SCIM value to map into metadata, Applivery follows these rules:
- If a namespace is specified, the system searches for the SCIM attribute inside that exact namespace/schema.
- If no namespace is defined, the system maps the first matching attribute key found in any schema.
- When a SCIM payload includes a value for a mapped custom attribute, Applivery automatically writes it into the user’s
metadata:- Key: The name defined in the
mappedAttributesentry. - Value: The resolved SCIM attribute value based on the mapping rules.
- Key: The name defined in the
Example of a namespace-based mapping #
SCIM payload #
{
"schemas": [
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:core:2.0:User",
"urn:company:params:scim:schemas:extension:custom:2.0:User"
],
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:core:2.0:User": {
"userName": "jane.smith"
},
"urn:company:params:scim:schemas:extension:custom:2.0:User": {
"employeeId": "EMP-4567",
"department": "Engineering"
}
}
Custom mapping configuration #
const mappedAttributes = [
{
name: "department",
attributes: [
{
namespace: "urn:company:params:scim:schemas:extension:custom:2.0:User",
key: "department"
}
]
},
{
name: "employeeCode",
attributes: [
{
namespace: "urn:company:params:scim:schemas:extension:custom:2.0:User",
key: "employeeId"
}
]
}
]
Result in user's metadata #
{
"metadata": {
"department": "Engineering",
"employeeCode": "EMP-4567"
}
}
Configure attribute mapping on Applivery #
Go to your Workspace > Settings (1) and open the Login providers (2) section. Then click Configure (3) next to the SAML option under the MDM Portal section.
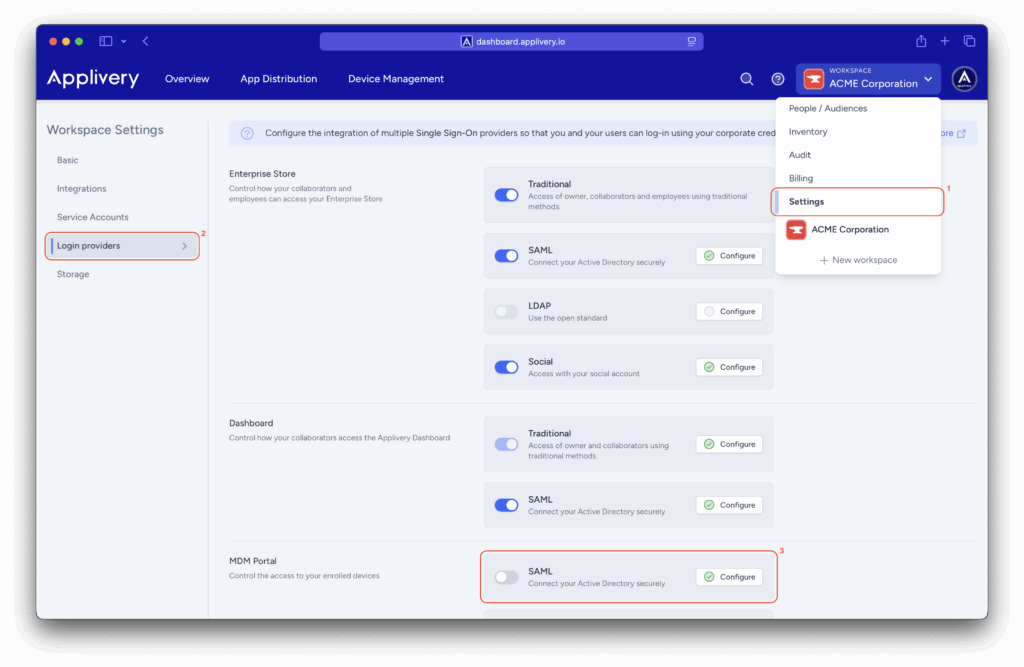
Scroll down to Step 3 and enter the appropriate namespace. You can determine the correct namespace based on the attribute type (Core, Enterprise, or Custom) and its value.
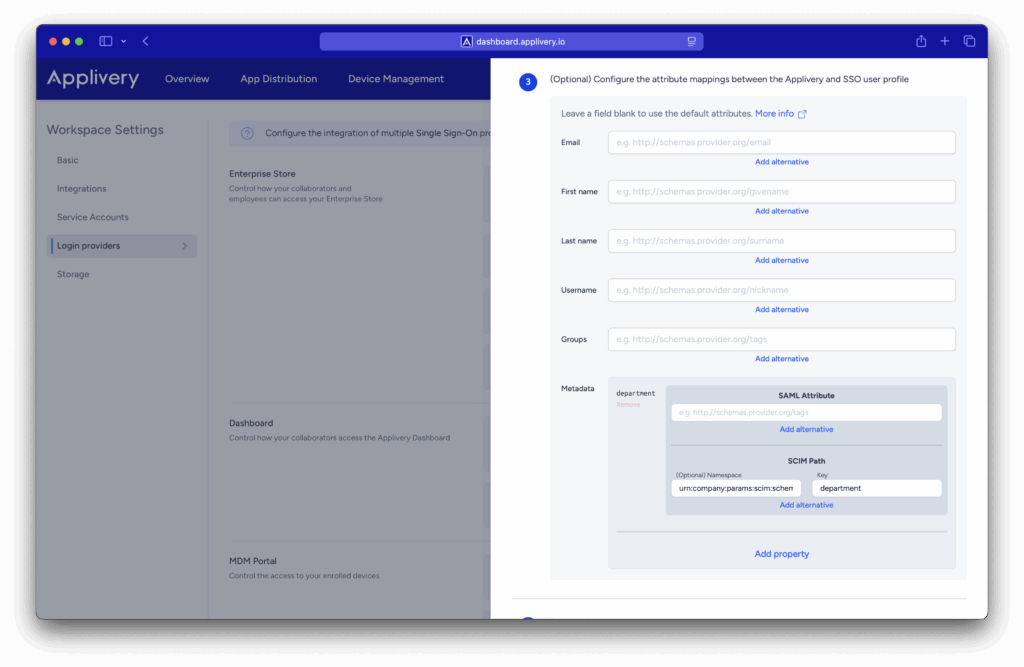
To save your changes, simply click Save. Once your IdP performs its next scheduled sync, the mapped attributes on both sides will begin populating each user’s metadata in Applivery.
To summarize:
- SCIM attributes can be mapped to user metadata using
mappedAttributes. namespacehelps disambiguate attributes when multiple schemas are involved.- Any unmapped SCIM attributes are stored in
attributesHistoryfor future reference. - This mapping system gives you full control over how user data is stored and leveraged downstream.