Android devices come equipped with powerful security features designed to protect user data and privacy. Chief among these is the keyguard, or lock screen, which appears before accessing the device’s home screen or apps and serves as the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Keyguard enforces secure authentication through PIN, password, pattern, or biometrics—like fingerprint or facial recognition—while also offering additional features such as notification display, camera shortcuts, and media controls directly on the lock screen.
Managing Android Keyguard and Lock Screen features allows IT admins to define which functions remain accessible before user authentication, enforce organizational security policies, and create a seamless user experience. With Applivery, admins can centrally configure lock screen behavior, customize which features are enabled, and ensure compliance across the device fleet, helping balance convenience and robust device protection.
Customizing Keyguard behavior #
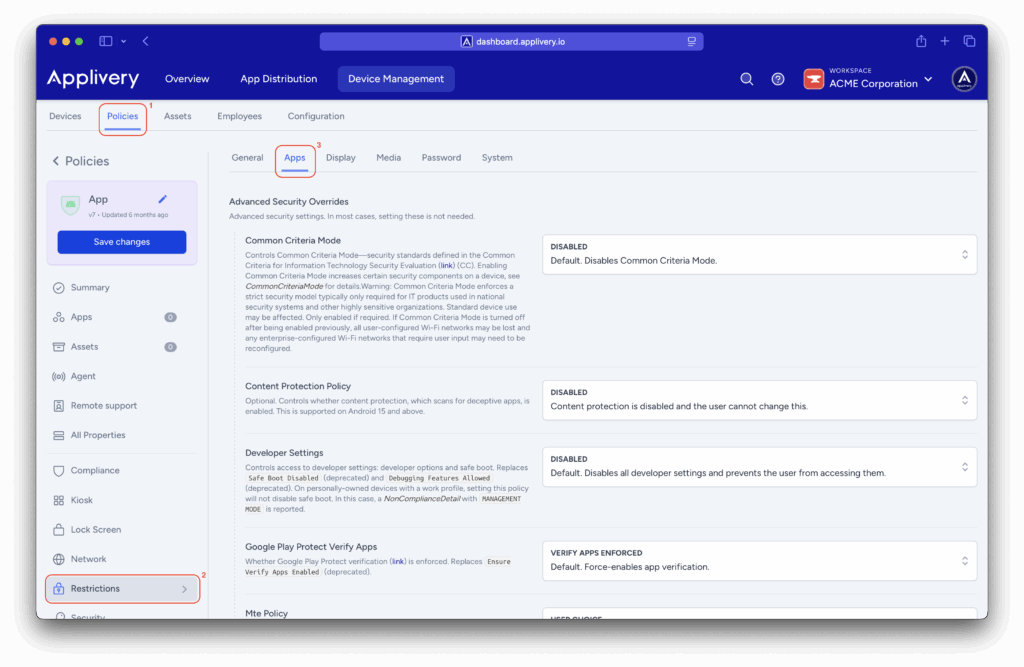
Once in the Applivery Dashboard, go to any of your Policies (1) (under Device Management > Policies). From the left side menu go to Restrictions (2) and locate the Apps (3) section.
Locate the Keyguard Disabled Features and click on + Add element to expand all the configuration fields:
- Camera: Disables the camera on secure keyguard screens, preventing access even if the lock screen normally allows it (e.g., the camera widget won’t be accessible).
- Notifications: Hides all notifications on secure keyguard screens. When enabled, no notifications—regardless of content—will appear.
- Unredacted notifications: Hides only sensitive or “unredacted” content on secure keyguard screens. The notification itself remains visible, but its details are concealed.
- Trust agents: Ignores trust agents that normally keep the device unlocked in certain conditions (e.g., when paired with a trusted smartwatch). When disabled, the device always locks regardless of active trust agents.
- Disable fingerprint: Prevents fingerprint authentication on the keyguard screen. Users must unlock using a PIN, password, or pattern.
- Disable remote input: On Android 6 and earlier, disables text entry in notifications on secure keyguard screens. Has no effect on Android 7 or later.
- Face: Disables facial recognition authentication on secure keyguard screens.
- Iris: Disables iris authentication on secure keyguard screens, preventing unlocking via iris scanner.
- Biometrics: Disables all biometric authentication (fingerprint, face, iris) on secure keyguard screens. This is a broader option than individual biometric controls.
- Shortcuts: On Android 14 and later, disables all lock screen shortcuts, preventing quick access to features like the camera or flashlight.
- All features: Deactivates all current and future keyguard features and customizations at once (e.g., camera, notifications, biometrics). Ideal for environments requiring strict control, such as kiosks, where users should only access the designated application.
Managing Keyguard features on Android devices is essential for controlling both security and user experience. By disabling specific features like biometric authentication, notifications, or shortcuts, you can tailor the device’s behavior to meet specific needs, whether that’s enhancing security in a corporate environment or optimizing a device for use as a digital kiosk.
Understanding these functionalities allows device administrators and app developers to implement robust security policies and ensure that users can only access the features they need. Ultimately, a well-configured keyguard not only protects the device from unauthorized access but also contributes to a more secure and controllable Android ecosystem. With the right tools and knowledge, the keyguard evolves from a simple lock screen into a powerful tool for device security management.