Applivery provides a unified platform to manage Apple, Android, and Windows devices in corporate environments. From enrollment to policies, automation, and resources, administrators can centrally control every aspect of Device Management.
Accessing the Applivery Dashboard #
To start managing your devices, log in to the Applivery Dashboard. Users with access are called Collaborators and have different permissions depending on their role. This ensures that tasks like device enrollment, policy assignment, and automation can be delegated while maintaining security and operational control.
Getting started with Applivery is straightforward. Once your workspace is created, you can immediately begin enrolling and managing your devices.
The Dashboard #
The Device Management Dashboard is organized into dedicated sections that allow administrators to monitor, enroll, configure, and automate Device Management across the organization.
From high-level fleet visibility to granular policy configuration, the dashboard centralizes all device operations into a structured and role-based interface.
Overview #
The Overview section is the first screen in your workspace and provides key metrics to quickly assess your device fleet. Here you can find information about:
- Total number of enrolled devices.
- Device status (active, inactive, or disabled).
- Most used models and OS versions.
- Battery levels.
- Compliance status.
These metrics allow administrators to detect trends, identify potential issues, and make data-driven decisions regarding Device Management.
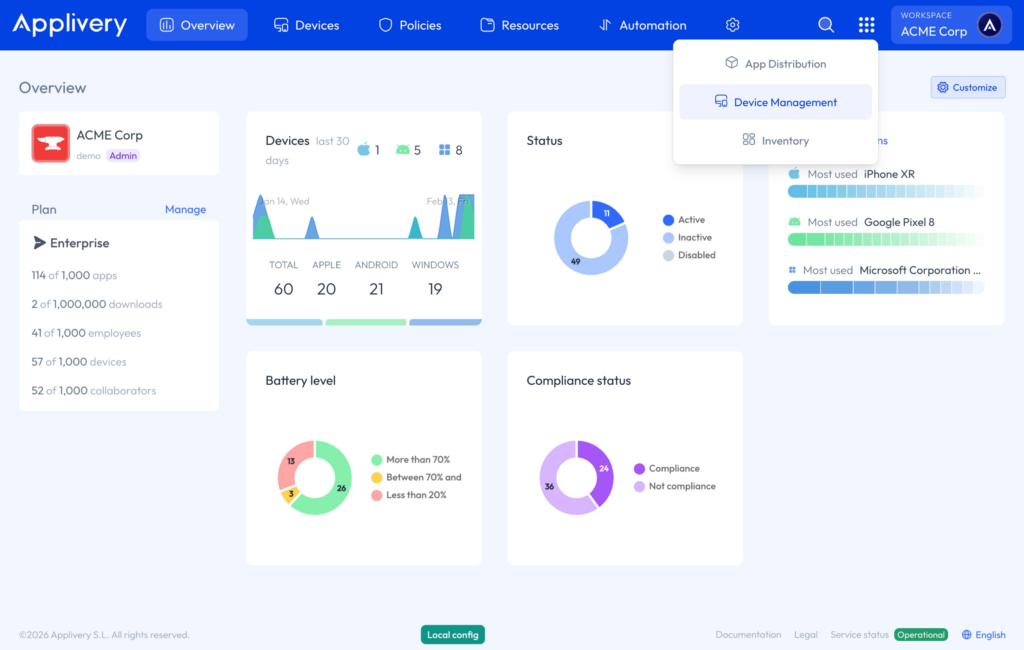
Devices #
The Devices section displays all devices currently enrolled in your workspace. Devices are listed according to segments created by workspace administrators. Access to devices is controlled based on the segment permissions assigned to each collaborator.
From this view, users can:
- Enroll new devices (Apple, Android, or Windows).
- Execute bulk actions, such as policy assignments or remote commands.
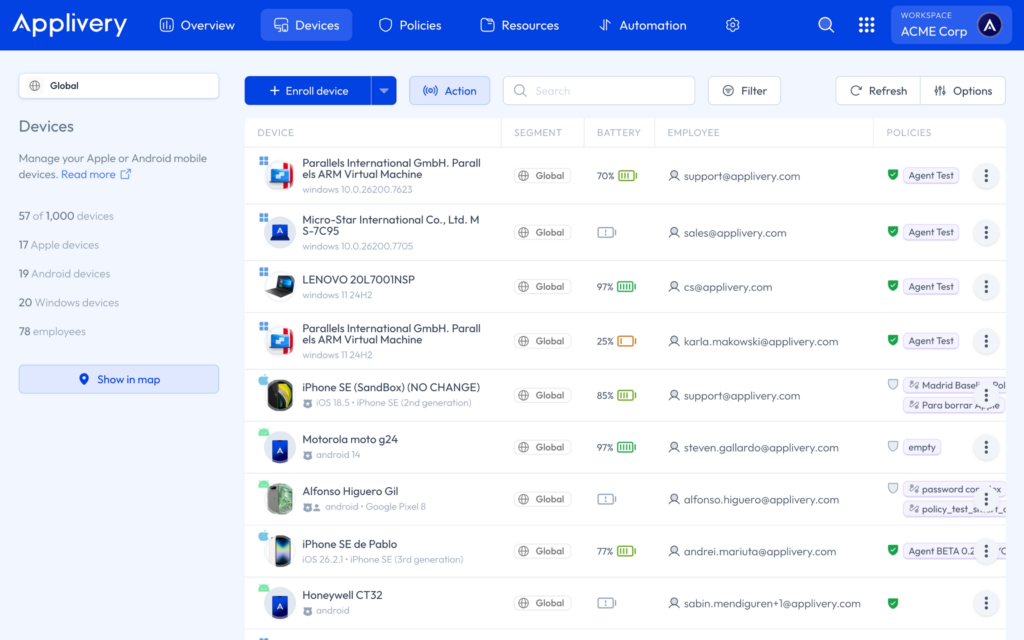
Policies #
A Policy is a collection of configurations that defines how a device behaves once it is managed. Depending on the platform, a policy may include:
- System restrictions and security settings (passcodes, encryption).
- Application installation rules.
- Scripts or automated actions.
- Integrations with security services.
- Kiosk mode settings.
The Policies section lists all policies available to your account. As with devices, visibility and access to policies depend on your workspace segment permissions. From here, administrators can create new policies or modify existing ones.
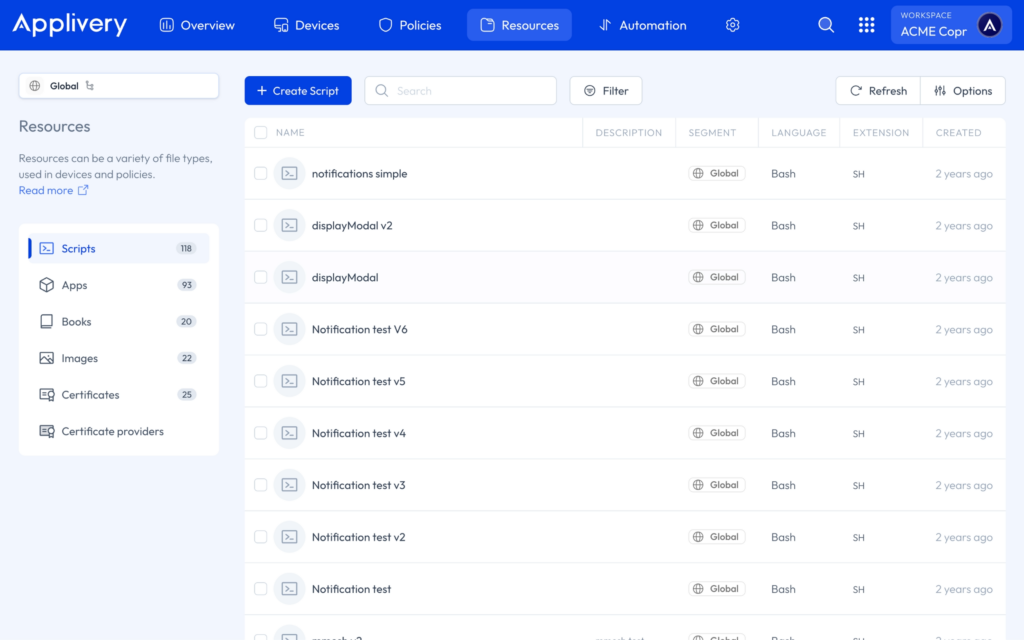
Resources #
The Resources section centralizes all deployable assets used across your Device Management workflows. These resources can be:
- Apps: Deploy custom-built or third-party applications to ensure device employees have access to the tools they need. Supported formats include
.ipa,.pkg,.msi,.msix,.appx, and.apk. This enables secure enterprise distribution of internal apps, line-of-business tools, and approved external software across managed devices. - Scripts: Automate operational tasks and system configurations by deploying bash scripts for macOS and powerShell scripts for Windows. Scripts can be used for software installation, system configuration changes, remediation actions, compliance enforcement, or maintenance tasks.
- Books: Distribute documentation and digital content in multiple supported formats, including
.pdf,.epub,.rtf,.rtfd,.txt.
- Images: Deploy image files in
.jpgand.pngto your Apple and Windows devices. Images can be used for branding, kiosk configurations, lock screen customization, or internal content distribution. - Certificates: Secure device communications and authentication by deploying digital certificates. Supported formats include
.p12,.der,.pem,.crt,.cer. Certificates are essential for Wi-Fi authentication, VPN access, email security, and secure application communication. - Certificate providers: Configure them to automate certificate issuance and lifecycle management. This allows devices to dynamically request and renew certificates through integrated identity or certificate authorities, improving security and reducing manual administrative overhead.
Automation #
The Automation section is organized by operating system and allows administrators to streamline device lifecycle management through automated workflows:
- Smart enrollments: They allow you to automate the device enrollment process based on predefined rules and conditions. You can define criteria that devices must meet during enrollment and automatically assign the appropriate policies based on those conditions. This ensures devices are configured correctly from the very beginning, without manual intervention.
- Device audiences: They allow administrators to create dynamic groups of devices based on specific attributes such as operating system, compliance status, model, or custom criteria. These audiences make it easier to target specific subsets of devices for configurations, policies, or deployments. To learn more about device audiences, refer to our documentation.
- Automation rules: They allow administrators to automatically execute actions when certain conditions are met. Each rule is linked to a Device audience. When a device matches the defined criteria, one or more predefined actions—such as policy assignments, app deployments, or configuration updates—are automatically triggered. This enables dynamic, large-scale Device Management without requiring manual operations. To learn more about Automation Rules, refer to our documentation.

These features allow IT teams to reduce manual tasks, maintain compliance, and ensure devices are configured consistently across the fleet.
Directory and Configuration #
The Directory and Configuration section centralizes identity management, access control, workspace segmentation, and operating system–specific settings within Applivery’s Device Management environment.
This section ensures that administrators can securely control who manages devices, which devices they can access, and how platform-specific configurations are applied across the organization.
- Collaborators: Users with access to the Applivery Dashboard. They can be assigned granular roles and permission levels depending on their operational responsibilities, such as full administrative control, Device Management permissions, policy creation and modification, and read-only access. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures operational security by limiting access to sensitive device actions and preventing unauthorized configuration changes.
- Device employees: End users who have one or more devices assigned to them. These users represent the human layer of your device fleet and are essential for device ownership tracking, compliance association, policy targeting and resource assignment (apps, configurations, books, etc.).
- Segments & Permissions: Segments allow administrators to logically divide the workspace into structured groups for granular control. They can be used to restrict collaborator access to specific subsets of devices, isolate environments (e.g., departments, regions, subsidiaries), control visibility of policies and resources, and delegate management responsibilities securely. Permissions are enforced based on segment membership, ensuring that administrators only manage the devices and configurations relevant to their scope. This structure is critical for large-scale or multi-entity deployments.
- Operating system configurations: This section also includes platform-specific configuration settings for each supported operating system (Apple, Android, and Windows). Depending on the platform, administrators can configure enrollment methods and platform integrations.